„Interface analysis"= function analysis!
1. Objective (Why?)
Goals:
- The functions for the systems and subsystems are shown in full diagram.
- The specifications of the data sheet are included.
Prerequisites:
2. Procedure (How?)
1. Identify all interfaces of the system to be viewed.
These can, for example, be subdivided into:
- mechanical interfaces
- hydraulic interfaces
- Pneumatic interfaces
- electric / electronic interfaces
- interfaces with the environment
- optical / haptic interfaces
2. If possible, identify and number these interfaces on the object / or model
3. Describe the functions at the interfaces. Use a simple sentence structure, e.g. noun - verb
3. Examples "Identification Interfaces"
1.1.1.1. Cassette (1) (Fig. 1)
* 1.1.1.1.a Carrying out the cassette(1)
* 1.1.1.1.b Position the cassette(1)
* 1.1.1.1.c Position the cassette in the system(1)
* 1.1.1.1.d Stacking the cassette(1)
* 1.1.1.1.e Ensure tamper protection(1)
* 1.1.1.1.f Allow unlocking(1)
* 1.1.1.1.g Connect the connector(1)
* 1.1.1.1.h Protect content(1)
* 1.1.1.1.i etc.(1)

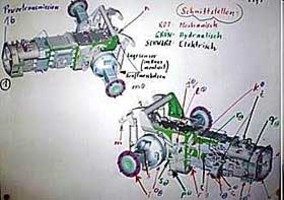
1.1.1.1.2.3 Drive train (1) (Fig. 2)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.a Transfer torque to the hydraulic system (1)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.b Receiving loads of front loaders (1)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.c Ensure mechanical and structual connection to the engine (1)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.d Transfer power from the motor (1)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.e Ensure mechanical connection of hydraulic pumps (1)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.f Transfer torque to wheels (1)
*1.1.1.1.2.3.g etc. (1)
3. Result
- Complete and systematic description of the interface functions
- Functional system understanding of the parties involved
- Input for the description of functional relationships (function networks)