Design Review Based on Failure Mode
1. Objective (Why?)
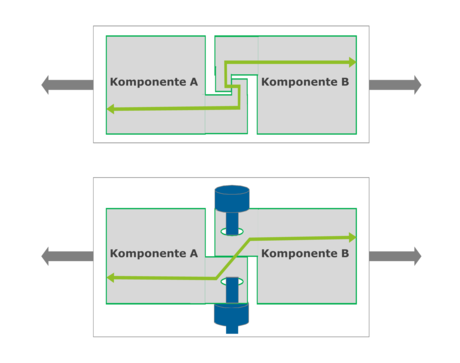
Function and interface X.
The functional transition at the interface X can be "solved" by constructive design of the components A and B.
However, the functional transition can also be realized with auxiliary components (bolt and nut) which are not themselves in the force flow.
Prof. Tatsuhiko Yoshimura (Toyota) came to the conclusion when applying FMEA in "Design Reviews" that the following aspects can complicate its application:
- FMEA does not have a specific focus on changes and their consequences.
- The complexity of the FMEA can interfere with the developers' focus on the changes.
- FMEA may steer developers' thoughts too quickly in one direction during the creative phase of the design change.
This motivated Prof. Yoshimura to develop an independent method, but one that is closely related to FMEA.
Objective of the DRBFM method:
- Identification of defects resulting from intended changes.
- Identification of resulting unintentional changes to the product and the process
2. Procedure (How?)
Strengths DRBFM:
- Least possible formalism.
- Concentration on problem solving by focusing on changes
- Stimulating creativity through appropriate work tools and procedures
FMEA and DRBFM contents are partially compatible. The two methods complement and enrich each other. Nevertheless, the orientation of the methods is different:
- FMEA is strong in identifying all potential causes (for potential non-performance of a function).
- DRBFM is strong in the identification of all conceivable consequences of a (desired) change.
Areas of application of DRBFM
- Changes to the system, subsystem, component
- Application projects and variants
- Changes in requirements and functions
- Changes in manufacturing
How it works!
- Assemble an interdisciplinary team.
- Realize a creative process in the context of the planned changes to achieve robust products and processes.
- Use the appropriate working tools for DRBFM, such as:
Change Checklist (Awareness Sheet)
- Contents/Objectives: Identification of intentional and resulting unintentional changes.
Change Comparison Table
- Contents/Objectives: Identification of the actual change by comparing the previous design and the changed design.
Function Focal Point Table
- Contents/Objectives: Representation of the original functions and the impact of the change on the functions of the product.
Change/Function Matrix (Change and Functions Concern Points Table)
- Contents/Objectives: Comparison of functions relevant to the customer and the intended and resulting unintended functions and changes, risk presentation.
DRBFM form
- Contents/Objectives: Presentation of changes, the resulting risks and consequences, and the measures developed.
History: DRBFM
Tatsuhiko Yoshimura developed the following method in 1997.The purpose is to find our errors, which occur as a result of intentional changes and the resulting unintentional changes in the product and process.
Features
- Less formalism, hence concentration on finding the problem
- The working means and the procedure should stimulate the creativity of the engineers
- DRBFM was integrated in the GD³ philosophy

What does GD³ stand for?


DRBFM Process
Procedural course of DRBFM
Analysis of the change (1-4)
- Observation of the desired changes and identification of undesired effects
Analysis of the risks (5-6)
- Discussion about the effects on internal and/or external customers
Developing and evaluating solutions (6/7)
- The objective is to achieve successfully the desired change and at the same time effectively minimizing the risks.
Defining measures (7)
- Based on verfications and validations
- Developing and tracking the measures
Success monitoring (8)
DRBFM working means
DRBFM-form sheet
- Includes all changes, the risks emerging from them and all measures
Checklist of changes (Awareness-Sheet)
- AInstructions to identify desired and resulting undesired changes
Table of changes (Change Comparison Table)
- Comparison of the design until now and the modified design, makes the actual change clear
Table of functions (Function Focal Point Table)
- Describes the effect of the changes on the product systematically
Matrix of changes/functions (Change and Functions Concern Points Table)
- Comparison of the functions relevant for the customer and the desired and resulting changes, thus shows the risks
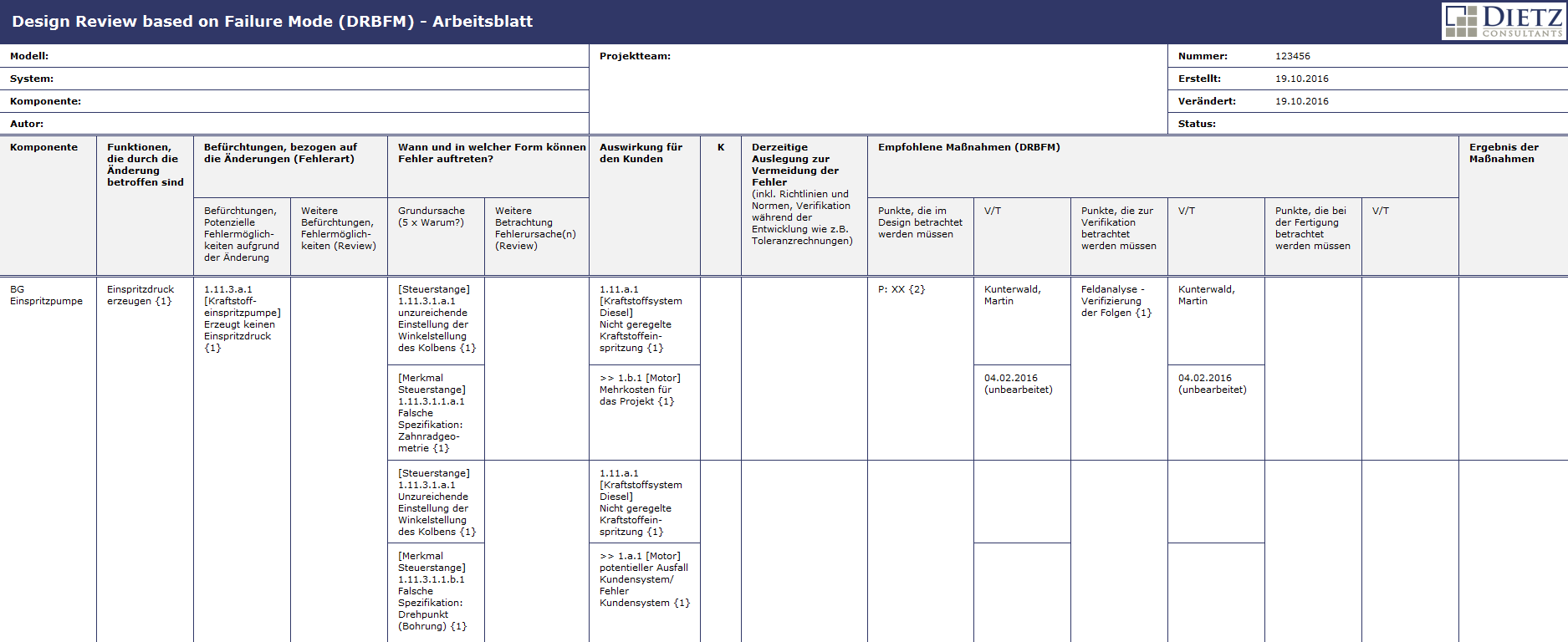
The DRBFM-form sheet

Analysis of the Cause - Failure – Effect relations.
- Presentation: Desired changes and the resulting undesired effects
- Presentation: Effects on the function and risks
- Determining measures for reducing the identified risks

Design Review
- Presentation: Specification of the required measures and determining the responsibility
- Presentation: Evaluation of the effectiveness of the determined measures
The DRBFM-form sheet – Analysis of the Failure chain
1 Description of the desired and undesired changes
- Part / Component name
- desired changes and reason for changes
- Undesired changes, which arise from the desired changes, with justification
Describe all specifications in detail
2 Description of the function
- Describe the function of the part as much precisely as possible
- Under which working conditions does the function occur?
- Describe all functions precisely
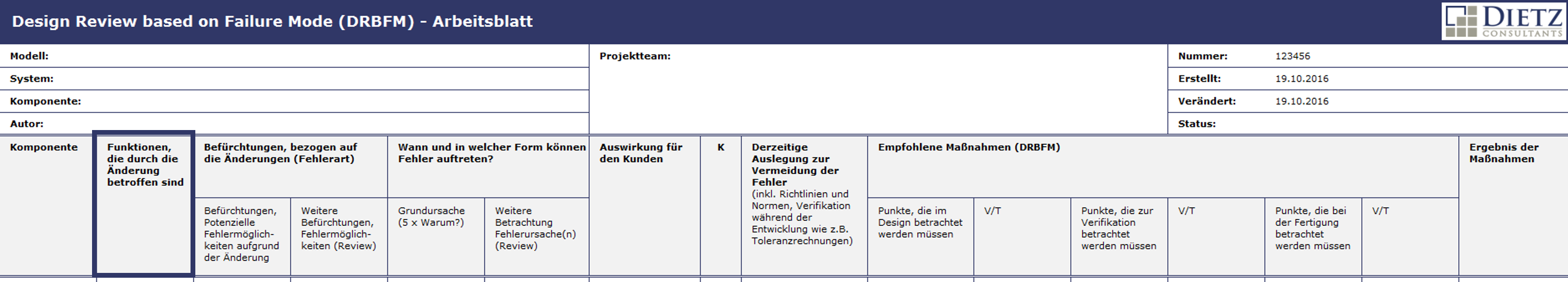
3. describe the error possibilities from the change
- Describe the risks exactly
- Collect other fears in teamwork.

4 Description of the Occurance and the Failure causes
- W-questions: When? / How often? / Where? / …
- Negating functions
- 5 x Why questions (W-method), in order to find out the true cause (measures are effective only if they are directed against the causes)

5 Consequences
- Which consequences arise for the defined customers?

6 Current measures to Prevent Failures
- Define measures
- Follow thereby the operating conditions and requirements
- When required, defined other measures (=>7)

7 Determined measures (Results of DRBFM)
- If Point 6: „Present measures“ are not sufficient, additional measures are developed
- Naming responsible persons and deadlines

8 Determining effectiveness of the measures
- For every measure from the DRBFM, the following is determined what was done, when and how and the results.